Create a multi-region universe
YugabyteDB Anywhere allows you to create a universe spanning multiple geographic regions.
For example, you can deploy a universe across Oregon (US-West), South Carolina (US-East), and Tokyo (Asia-Northeast).
Prerequisites
Before you start creating a universe, ensure that you have created a provider configuration as described in Create provider configurations.
Create a universe
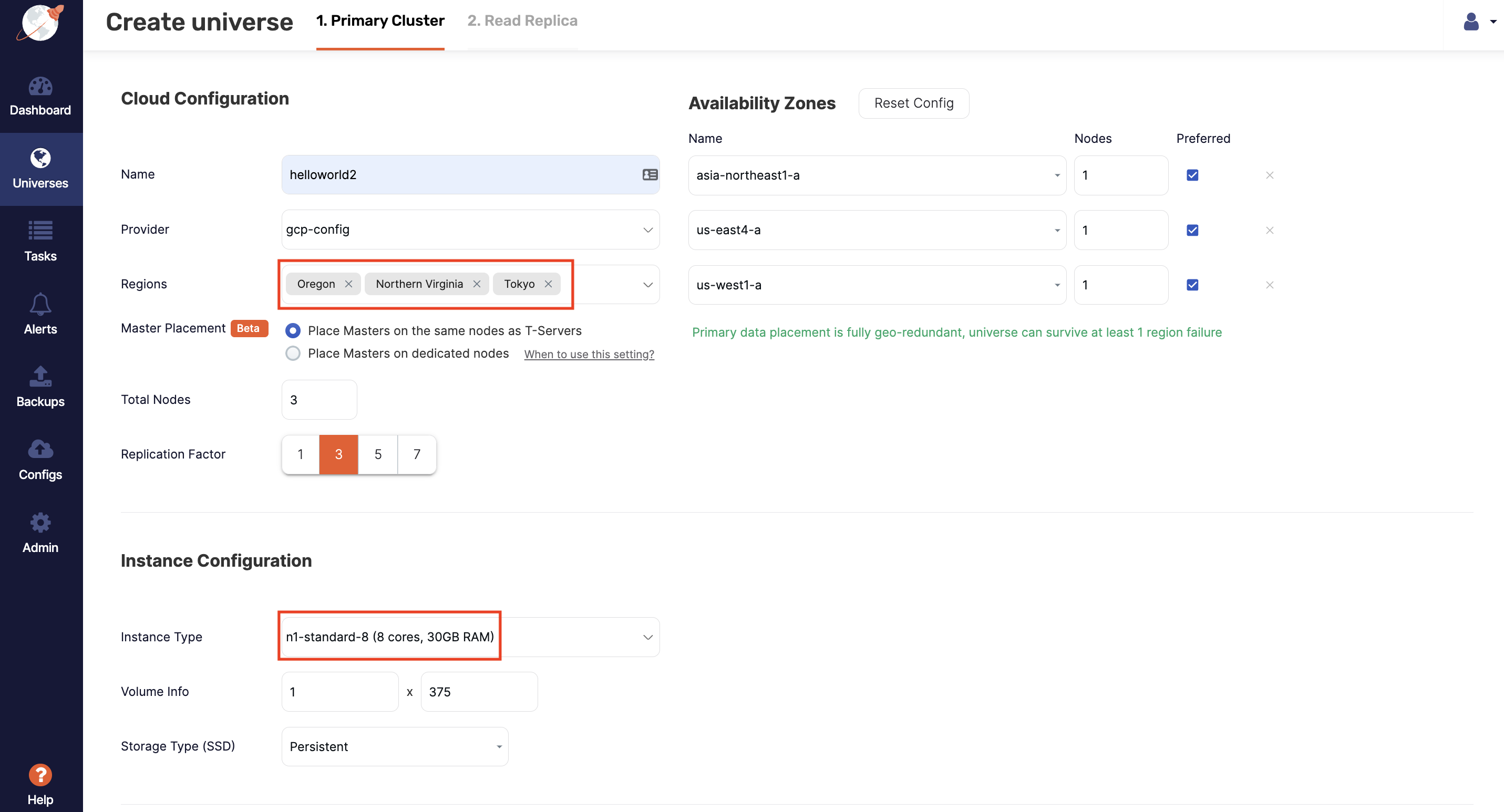
After you have configured a cloud provider, such as, for example Google Cloud Provider (GCP), navigate to Universes, click Create Universe, and enter the following sample values:
-
In the Name field, enter helloworld2.
-
In the Provider field, select the cloud provider you configured.
-
Use the Regions field to select the regions where you want to deploy nodes.
-
Choose the Linux version to be provisioned on the nodes of the universe.
-
In the Instance Type field, select a suitable instance type; these will vary depending on the cloud provider.
-
Provide any other desired settings for Security Configurations, and Advanced Configuration.
-
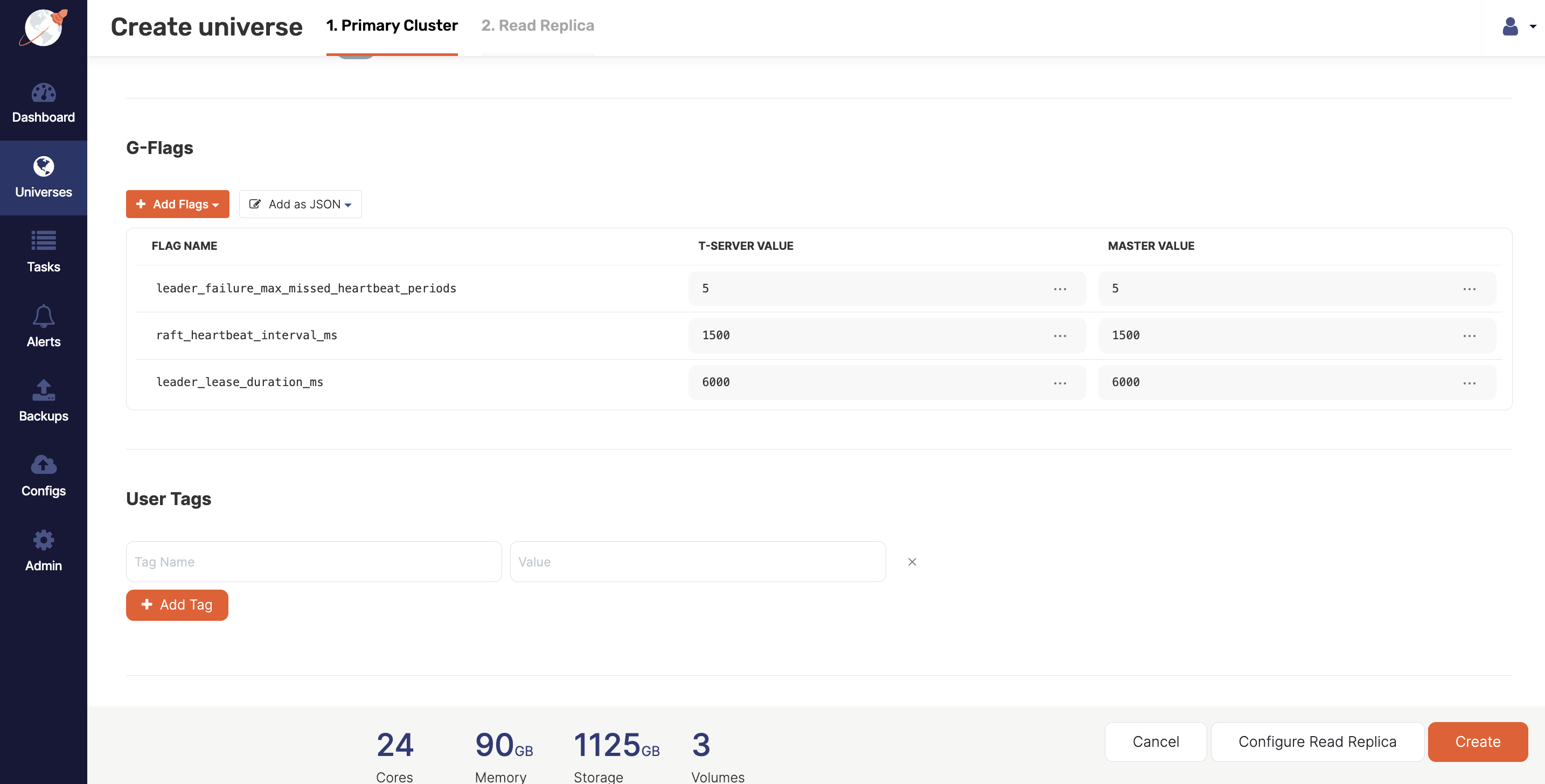
For G-Flags, click Add Flags, Add to Master, and add the following flags for Master:
leader_failure_max_missed_heartbeat_periods 5 raft_heartbeat_interval_ms 1500 leader_lease_duration_ms 6000And add the following flags for T-Server:
leader_failure_max_missed_heartbeat_periods 5 raft_heartbeat_interval_ms 1500 leader_lease_duration_ms 6000Note that because the data is globally replicated, RPC latencies are higher; these flags are used for increasing the failure detection interval in a higher RPC latency deployment.
-
Click Create.
Note that all YugabyteDB universes created using YugabyteDB Anywhere have the YB Controller automatically installed on their nodes. The YB Controller works in the background to speed up backup and restore of universes.
Examine the universe
When the universe is created, you can access it via Universes or Dashboard.
To see a list of nodes that belong to this universe, select Nodes. Notice that the nodes are distributed across geographic regions.
You can also verify that the instances were created in the appropriate regions by clicking on the node name to access the cloud provider's instances page. For GCP, you navigate to Compute Engine > VM Instances and search for instances that contain helloworld2 in their name.
Run a global application
Before you can run a workload, you need to connect to each node of your universe and perform the following:
- Run the
CassandraKeyValueworkload. - Write data with global consistency (higher latencies are expected).
- Read data from the local data center (low latency timeline consistent reads).
The first step is to navigate to Nodes, click Connect, and then use the Connect dialog to provide the required endpoints.
Connect to the nodes
You start by creating three Bash terminals. Then, for each node, click its corresponding Actions > Connect, copy the sudo command displayed in the Access your node dialog, and paste it into a Bash terminal.
With the goal of starting a workload from each node, perform the following on every terminal:
-
Install Java by executing the following command:
sudo yum install java-1.8.0-openjdk.x86_64 -y -
Switch to the
yugabyteuser by executing the following command:sudo su - yugabyte -
Export the
YCQL_ENDPOINTSenvironment variable (IP addresses for nodes in the cluster) by navigating to Nodes, clicking Connect, then using the Connect dialog to copy endpoints under the relevant category, and finally pasting this into a Shell variable on the database nodeyb-dev-helloworld2-n1to which you are connected, as per the following example:export YCQL_ENDPOINTS="10.138.0.3:9042,10.138.0.4:9042,10.138.0.5:9042"
Run the workload
Run the following command on each of the nodes, substituting REGION with the region code for each node:
java -jar /home/yugabyte/tserver/java/yb-sample-apps.jar \
--workload CassandraKeyValue \
--nodes $YCQL_ENDPOINTS \
--num_threads_write 1 \
--num_threads_read 32 \
--num_unique_keys 10000000 \
--local_reads \
--with_local_dc <REGION>
You can find the region code of each node by navigating to Nodes and looking under the CLOUD INFO column: the first part before the slash indicates the region. For example, us-west1.
Check the performance
The application is expected to have the following characteristics based on its deployment configuration:
- Global consistency on writes, which would cause higher latencies in order to replicate data across multiple geographic regions.
- Low latency reads from the nearest data center, which offers timeline consistency (similar to asynchronous replication).
You can verify this by navigating to Metrics and checking the overall performance of the application.