SQL Workbench/J
SQL Workbench/J is a free, DBMS-independent, cross-platform SQL query tool that also works with YugabyteDB. SQL Workbench/J is written in Java and should run on any operating system that provides a Java Runtime Environment (JRE).
SQL Workbench/J has the following main focus:
- Running SQL scripts, either interactively or as a batch
- Rich support for importing and exporting datasets
- Editing, inserting, and deleting data directly in the query result view
- Running queries in console mode
In this section, you'll learn how to connect SQL Workbench/J with all of the YugabyteDB APIs on a local cluster. SQL Workbench/J works without any issues with YugabyteDB because the YugabyteDB APIs are compatible at the wire protocol level with databases already supported by SQL Workbench/J.
Before you begin
To use SQL Workbench/J with YugabyteDB, you need to have YugabyteDB up and running, the required Java Runtime Environment (JRE), and the required PostgreSQL JDBC driver.
YugabyteDB
Your YugabyteDB cluster should be up and running. Refer to YugabyteDB prerequisites.
Java runtime environment (JRE)
SQL Workbench/J requires a Java runtime (or JDK) for Java 8 or later. JRE and JDK installers for Linux, macOS, and Windows can be downloaded from OpenJDK, AdoptOpenJDK, or Azul Systems.
For details on the JRE requirements, see the prerequisites section in the SQL Workbench/J Getting started page.
PostgreSQL JDBC driver
To connect SQL Workbench/J to a YugabyteDB cluster, you need the PostgreSQL JDBC driver installed. To download the current version that supports Java 8 or later, go to the PostgreSQL JDBC Driver Download page.
SQL Workbench/J
To install, go to the SQL Workbench/J website, download the distribution package for the operating system on your client computer, and extract the archive into a directory of your choice.
The application is now ready to run — no further steps are necessary. For details, see Installing and starting SQL Workbench/J in the SQL Workbench/J user manual.
Configure SQL Workbench/J
Configure the PostgreSQL driver
YugabyteDB is PostgreSQL-compatible, so when working with SQL Workbench/J, use the PostgreSQL JDBC Driver.
-
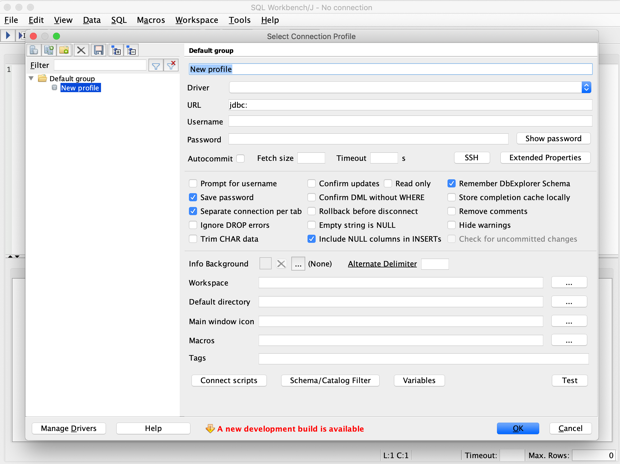
Launch the SQL Workbench/J application. The Select Connection Profile pop-up window appears.
-
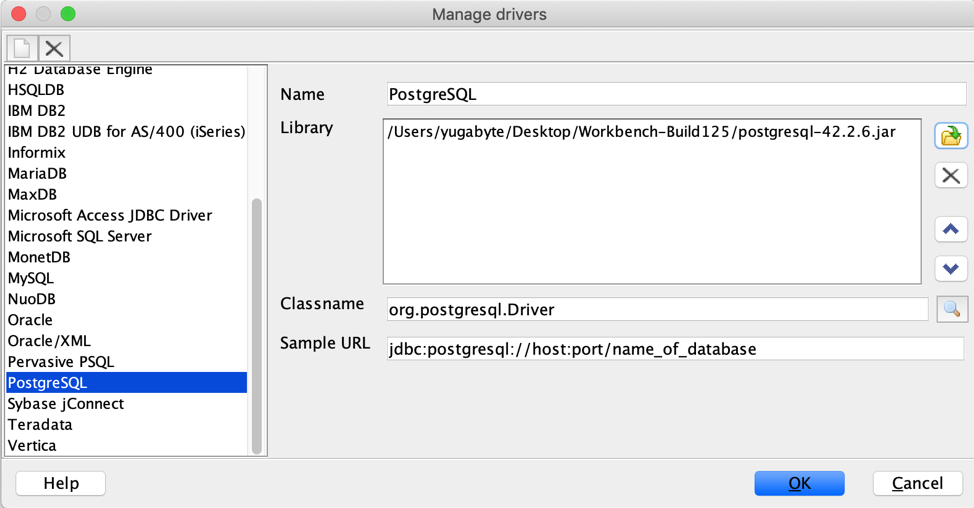
Click Manage Drivers (in the lower left of the window) to open the Manage Drivers window.
-
In the list of drivers, select
PostgreSQLand then edit the fields for the driver:-
Name:
PostgreSQL (for YugabyteDB) -
Library: Displays the location of the PostgreSQL JDBC driver's JAR file. [For a new configuration, browse to the location of the file and click Choose.] When installed, the default location of the JRE or JDK is:
\Library\Java\Extensions\<jdbc-driver>.jar` -
Classname:
org.postgresql.Driver -
Sample URL:
jdbc:postgresql:127.0.0.1:5433/name_of_database(based on YugabyteDB default values). When opening the driver configuration initially, this field displaysjdbc:postgresql://host:port/name_of_database
-
-
Click OK. The Manage drivers window closes and returns you to the Select Connection Profile window.
You have now configured the PostgreSQL JDBC driver to work with YugabyteDB and can now create a connection profile.
For more information, see:
- JDBC Drivers in the SQL Workbench/J user manual.
- PostgreSQL JDBC Driver documentation.
Create a YugabyteDB connection profile
You need to create a connection profile for each database you use and you can always get to the Select Connection Profile window from the menu by selecting File > Connect window.
- In the Select Connection Profile window, click Create a new connection profile. A new profile is created.
- Replace
New profilewith a meaningful name for the connection profile. Because you need a separate profile for each database connection, include the database name in your profile name. - For Driver, select
PostgreSQL (for YugabyteDB) (org.postgresql.Driver). - For URL, replace
name_of_databasewith the name of the database you want to connect to. - For Username, enter
yugabyte, or the user name you will be using. - For Password, leave the field empty unless YSQL authentication is enabled.
- Select Autocommit. In PostgreSQL and YugabyteDB,
AUTOCOMMITis on by default. - Click Test to verify that the connection works successfully.
- Click OK. The SQL Workbench/J default window appears. Your connection is now ready to be used.
That's all of the settings you need to start using the connection. For details on configuration profiles, see Connecting to the database in the SQL Workbench/J user manual.
What's next
Now that you know how to configure SQL Workbench/J to work with your YugabyteDB databases, you can start exploring the features of SQL Workbench/J. For details on using SQL Workbench/J, see SQL Workbench/J User's Manual.
If you're looking for sample databases to explore YugabyteDB using SQL Workbench/J, see Sample data.